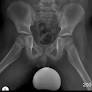
The frog leg position, often referred to as the 'frog leg' view or 'frog leg lateral view', is a special radiographic imaging technique used to evaluate the hip joints and the surrounding structures in neonates and toddlers. This view is obtained by having the patient lying supine (face up) with their outer thighs externally rotated, flexed, and abducted (turned outward) away from the midline of the body. The purpose of this examination is to assess the stability and function of the hip joints, particularly in the context of known or suspected hip dysplasia or Perthes disease.
Normal Development and the Frog Leg Position
During intrauterine development, neonates typically assume various fetal positions that are influenced by factors such as the available space within the uterus and the baby's own movements. In about half of all deliveries, the胎位(birth position) may be breech, meaning the baby's feet or buttocks are the first part of the body to emergence from the birth canal. This position can, in turn, place the baby's legs in a 'frog leg' configuration due to the outward curvature of the thighs.
This normal positioning of the legs usually resolves within the first few months of life as the baby gains muscle strength and flexibility. However, in some cases, the frog leg position may persist or be associated with other clinical signs, such as limping or difficulty walking, which could indicate a more serious condition such as hip dysplasia or Perthes disease.
The Importance of the Frog Leg Position in Neonatal Hip Assessment
The frog leg position is a crucial tool in the armamentarium of diagnostic imaging for assessing the neonatal hip. This view provides a direct view of the anterior and posterior aspects of the髋关节, including the acetabulum (socket) and the head of the femur (upper arm bone), as well as the intertrochanteric region, which is the area between theGreater Trochanter and Lesser Trochanter of the femur.
By evaluating the alignment and motion of these structures, the frog leg position能够帮助 healthcare professionals identify potential concerns such as hip dislocation, subluxation (partial dislocation), or instability. These issues can lead to altered mechanics of the hip joint and may result in persistent pain, reduced range of motion, or a variety of other complications.
Techniques and Interpretation
To obtain the frog leg position, the baby must be carefully positioned in a supine position with both legs extending forward and abducted. The examiner places their hands on either side of the affected leg to gently abduct the leg and apply varus stress to the knee joint. Palpating the lateral upper thigh and the trochanter region can help identify differences in joint space width, which may suggest laxity or instability in the hip socket.
If there are two or more millimeters ofdifference in the measurement between the affected and non-affected sides, this is often considered significant and may indicate the need for further evaluation or intervention.
Complications and Risks
Despite its utility, the frog leg position does carry certain risks and complications, particularly for newborns who are particularly small or fragile. The repeated pressure and stress associated with this imaging modality can lead to fractures or other injuries to the growing skeleton, such as hip fracture or periprosthetic hip fracture.
Moreover, exposure to radiation poses a potential risk, and the need to position the baby in a difficult position can increase the likelihood of motion artifact, which can distort the images and interfere with the diagnostic accuracy of the examination.
##The frog leg position is a valuable tool in the diagnostic evaluation of neonatal hip conditions. It provides a wealth of information on the structure and function of the hip joints, helping healthcare professionals to identify and manage a wide range of conditions that affect this delicate area of the body. While the frog leg position is generally safe and effective, it is important to consider the potential risks and take appropriate precautions to minimize any adverse effects. By maintaining a low threshold for clinical suspicion and prioritizing the safety and well-being of the patient, healthcare professionals can use this valuable imaging modality to guide the best course of action for their patients.