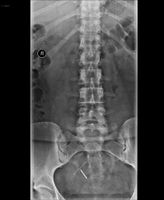
Intrauterine Devices and Their Visualization in Ultrasound
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are widely used as a form of contraception worldwide. They are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy by thinning the endometrial lining, preventing sperm motility, and preventing implantation. IUDs come in two main types: non-hormonal and hormonal. Non-hormonal IUDs are made of copper or alloyed with gold/silver, while hormonal IUDs, such as Mirena, release a synthetic hormone that affects the endometrium and suppresses ovulation.
Visualization of IUDs in Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the most commonly used method for confirming the placement and monitoring the position of IUDs. Transvaginal ultrasound is the preferred approach for initial placement and follow-up, as it provides better imaging of the endometrial cavity and avoids radiation exposure. Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound can provide more detailed imaging, especially in detecting malpositions and embedments.
Problems Associated with IUDs
Despite their effectiveness, IUDs can sometimes become malpositioned or Embedded within the myometrium, causing pain, bleeding, and other complications. These may include expulsion (IUD passing through the cervical os), displacement (IUD rotating out of the fundal position), embedding (IUD penetrating the myometrium without extending through the serosa), and perforation (IUD penetrating both the myometrium and serosa). Ultrasound plays a crucial role in diagnosing these problems and managing their complications.
management of malpositioned and embedded iuds
Management of malpositioned and embedded IUDs depends on the severity of the problem and the presence or absence of symptoms. For lightly positioned IUDs, observation may be adequate, while for more severe cases, an outpatient procedure with a forceps or special equipment might be necessary. Additionally, hysteroscopic visualization and repair may be required.
Impact of IUDs on reproductive health
IUDs can have significant impact on reproductive health, including reducing the risk of unplanned pregnancies and potentially influencing menstrual cycles. Additionally, certain types of IUDs may reduce the risk of endometriosis and ovarian cancer. However, IUDs may also have side effects, including menstrual irregularities, heavier bleeding, and pain, which may affect patients' quality of life., ultrasound is a powerful tool for confirming the placement and monitor the position of intrauterine devices. Understanding the imaging characteristics of properly and incorrectly positioned IUDs is essential for accurate management of complications. Familiarity with ultrasound findings of malpositioned and embedded IUDs can guide appropriate patient care and treatment.