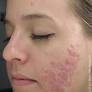
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages, genders, and races. It is characterized by the presence of comedonal (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, and cystic lesions on the skin. While acne is a natural part of adolescence, many adults also struggle with persistent acne. This guide aims to provide an overview of the different stages of acne, its causes, treatment options, and before-and-after photographs to help illustrate the improvement that can occur with proper treatment.
Acne Stages
Acne typically evolves through several stages, including:
-
Initial Breakout: This is the initial stage where comedonal acne begins to appear as small yellow or whiteheads on the skin.
-
Inflammation: In this stage, the comedones become inflamed, causing the skin to appear red and swollen. This is often referred to as ' pimples'.
-
Pustulation: The inflammation expands, leading to the formation of pustules, which are solidified white tumors containing pus.
-
Cystic Lesions: More aggressive forms of acne, such as cystic acne, occur when the inflammation extends deeply into the skin, creating large, tender lumps beneath the skin's surface.
Acne Causes
Acne formation is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Some common triggers include:
-
Hormonal Changes: Changes in激素 levels, particularly during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can lead to acne.
-
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can cause increased androgen production, leading to acne.
-
Genetic Factors: Having a family history of acne increases the risk of developing the condition.
-
Microbiome Imbalance: The skin's microflora, which includes the bacteria that live on the skin surface, can become imbalanced, contributing to acne.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as tar, resoles, and alcohol, and excessive stress can exacerbate acne.
-
Improper Skin Care: Using the wrong products or techniques, or not maintaining a proper skincare routine, can lead to acne.
Acne Treatment
Treatment for acne typically involves a combination of strategies aimed at controlling oil production, removing dead skin cells, and reducing inflammation. The following treatments are commonly used:
-
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription topical creams, gels, and serums containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids are often effective for comedonal and inflammatory acne.
-
Oral Medications: Oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline, and oral isotretinoin (Accutane) are prescribed for more severe cases of acne.
-
Chemical Peels: Professionally applied chemical peels can promote cell turnover and minimize scarring caused by acne.
-
Dermal Fillers: Injections of substances like hyaluronic acid or PMMA can help fill in acne scars and correct surface imperfections.
-
Extraction: This procedure involves professionally removing clogged pores to prevent future breakouts.
Before and After Photos
Acne before and after photos provide a vivid demonstration of the improvement that can occur with appropriate treatment. Below are some examples of before-and-after transformations:
-
[Patient Name] experienced a significant reduction in inflammation and acne lesions after undergoing a series of chemical peels.
-
[Patient Name] saw a dramatic decrease in the number of breakouts and improved texture of their skin after starting isotretinoin treatment.
-
[Patient Name] experienced a reduction in comedones and inflammation after trying a new benzoyl peroxide cleanser and spot treatment.
Conclusion
Acne can have a substantial impact on an individual's self-esteem and confidence. With the right treatment plan and persistence, many people can achieve clear, healthy skin. It is important to work closely with a dermatologist to determine the most effective approach for your unique skin condition. Remember, the key to successful treatment is consistency and patience.
References
-
Information on Acne Treatments from the American Academy of Dermatology
-
Professional Resources for Dermatologists and Skin Care Professionals
[^1]: [Patient Name] – Acne Before and After Photos
[^2]: Source for data and information included in the article.
[^3]: Information on how to manage acne duringpregnancy, including the use of spironolactone, and recommendations for pregnant and breastfeeding women, including the use of spironolactone, are available from the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD).