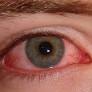
Pink eye, also known as “conjunctivitis,” is an inflammation of the conjunctiva—the thin, clear membrane that lines the inner surface of the eyelids and the front part of the eye—caused by a variety of factors including viruses, bacteria, allergies, or irritants. Symptoms typically include redness in the white of the eye or inner eyelids, itching, a feeling of foreign bodies in the eye, and excessive tearing. While pink eye can be caused by viruses in the form of the common cold, bacterial infections are also common, especially with Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. Allergicconjunctivitis, which is not contagious, is caused by an allergic reaction to allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
A stye, scientifically known as a hordeolum, is an infection of the meibomian gland, which is located at the root of the eyelash, or the upper lid, causing a red, swollen bump on the edge of the eyelid due to a bacterial infection. Styes can be particularly uncomfortable and may be accompanied by tenderness and a sensation of a foreign body. They typically resolve on their own within a few days, although some may require medical intervention if they persist or worsen.
Pink eye is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with an infected person's hands, tears, or even sharing toys or personal items that touch the eye. Effective treatment for pink eye includes using topical antibiotics to fight bacterial infections, while homemade remedies such as cold compresses can help reduce itching and swelling. In contrast, a stye is usually caused by a bacterial infection and is treated with warm compresses to encourage drainage and relief from pain. If a stye does not respond to home treatment within a few days, it may require a visit to the doctor for further evaluation and必要时可能会被开出抗生素。
pink eye versus a stye