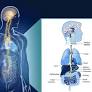
Vagal nerve constipation refers to persistent or recurrent constipation caused by dysfunction of the vagus nerve, a key nerve connecting the brain and the intestines. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in regulating digestive systems, and its imbalance can lead to various digestive problems, including constipation. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy, function, and conditions related to the vagus nerve, as well as the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for vagus nerve constipation.
An Overview of the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, commonly known as the "wandering nerve," is one of the 12 cranial nerves and stretches from the head to the abdomen. It serves as a communication channel between the brain and the organs of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis. The vagus nerve is composed of both sensory and motor fibers, allowing it to detect various external stimuli and send signals to the brain.
Functions of the Vagus Nerve
One of the primary functions of the vagus nerve is to regulate digestive functions. It contains a vast array of sensory cells that detect the presence of food in the stomach and intestine, regulating the urge to defecate.
Types of Vagal Nerve Constipation
Idiopathic Vagal Nerve Constipation
Idiopathic vagal nerve constipation refers to consistent or recurrent constipation where the underlying cause is unknown.
Drug-Induced Vagal Nerve Constipation
Drugs or medications, such asopioids, anticholinergics, and sedatives, can cause ileus or constipation due to their effect on intestinal smooth muscle.
Diagnostic Measures
Diagnosing vagus nerve constipation typically starts with a thorough history and physical examination. Following this, your doctor may recommend imaging tests like CT scans or MRI scans to rule out structural causes. Additionally, upper endoscopy and fecal occult blood testing may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for vagus nerve constipation depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Some of the common treatment modalities include:
Medications
Anti-spasmodics like mebeverine and simeticone may help relax the smooth muscle of the肠道 and improve constipation.
Laxatives
Lubiprostone and linaclotide are synthetic stimulants of the肠道's chloride channels that increase secretion of electrolytes and water leading to a more frequent bowel movement.
Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS)
This is a medical procedure in which electrodes are placed on the left upper arm skin to send gentle electrical impulses to the left vagus nerve. These impulses travel to the brain stem and vagus ganglion. VNS has been shown to promote smooth muscle contractions in the肠道 and enhance the release of gastrin, thereby stimulating contractions.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Besides medication and VNS therapy, making certain lifestyle and dietary changes can also help alleviate vagus nerve constipation such as:
• Incorporating physical activity and increasing fiber intake into your diet
• Consuming plenty of liquids consistently throughout the day.
• Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
##Vagal nerve constipation is a prevalent digestive problem that can significantly impact overall quality of life. It is caused by disturbances in the vagus nerve's function and may result from idiopathic or drug-induced factors. Treatment methods for vagus nerve constipation may Include medication, lifestyle changes and Vagal nerve stimulation. Patients experiencing this problem are recommended to consult with healthcare professionals who may tailor treatment options specific to their individual needs after conducting a thorough evaluation and gathering a detailed history.
References: