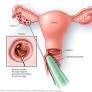
Overview
Egg retrieval is a medical procedure code that refers to the removal of eggs from the ovary. This procedure is most commonly performed as part of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment. The egg retrieval needle is a crucial tool used in this process, and knowing the features and specifications can help ensure the procedure runs smoothly and safely.
Function
The primary function of the egg retrieval needle is to aid in the removal of eggs from the follicles within the ovarian tissue. The egg is then extracted through a small incision in the卵巢 using an ultrasonic guidance system. The egg retrieval needle is designed with three main components:
-
Tip: The tip of the egg retrieval needle is ground flat to a sharp edge. This design allows for minimal trauma during the procedure, which can help reduce pain and the risk of injury to the ovarian tissue.
-
Body: The body of the egg retrieval needle is typically constructed from stainless steel or other durable materials. It is designed to withstand the rigors of the procedure and maintain its shape and integrity.
-
Hub: The hub of the egg retrieval needle is the point where the needle attaches to the irrigation source or aspiration pump. It is designed to be durable and securely attached to ensure smooth operation during the egg retrieval process.
Characteristics
Key characteristics of egg retrieval needles include:
-
Diameter: The diameter of the egg retrieval needle affects the size of the follicle it can aspirate. Smaller gauge needles (lower G numbers) are better suited for women with a low response to medication or those having natural cycles, as they can be easier to insert and remove from the follicle.
-
Length: The length of the egg retrieval needle typically ranges from 30 to 60 centimeters. The longer the needle, the further into the ovarian parenchyma it can reach. Long needles may be necessary in conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) where there is a significant amount of ovarian tissue to mobilize.
-
Aspiration Line: The aspiration line, also known as the aspiration channel, is the part of the needle that connects the tip to the hub. It carries the extracted eggs away from the follicle. Unlike the body of the needle, the aspiration line does not typically contain any irrigation solution.
-
Gauge: The gauge of the egg retrieval needle, expressed in G (gauge), indicates the size of the hole it creates. Smaller gauges (e.g., 16G or 18G) result in smaller incisions, which can be less painful and cause less trauma to the ovarian tissue.
-
Material: Most egg retrieval needles are made from stainless steel, which is strong, durable, and easy to clean and sterilize. Some needles may also be coated with a medical grade material, such as polyethylene, to reduce friction during insertion and extraction.
Safety Considerations
When performing an egg retrieval, it is important to consider the potential risks associated with the procedure. These risks can include:
-
Pain: Egg retrieval can be a discomforting procedure, and patients may experience pain or discomfort during or after the procedure.
-
Bleeding: While rare, there is a small risk of bleeding at the site of the incision.
-
Infection: The risk of infection at the site of the procedure is low if proper aseptic techniques are followed during the preparation and performance of the procedure.
-
损伤: There is a risk of damaging the ovarian tissue or structures nearby, including the ureter (which is a potential risk for female patients undergoing bilateral procedures).
To minimize these risks, careful preoperative preparation, including a comprehensive discussion with the healthcare provider, thorough preparation for the procedure, and monitoring during and after the operation, are essential.
##Egg retrieval needles are essential tools used in the field of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Understanding the different types of eggs and needles available, their characteristics, and safety considerations can help ensure a smooth and successful outcome in the procedure. Always consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing any fertility treatment or surgical procedure.