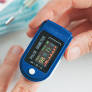
A pulse oximeter is a medical device that measures the oxygen saturation of the blood, which is the percentage of hemoglobin that is carrying oxygen. It is typically used to monitor patients in hospitals and emergency rooms, but it can also be used at home by individuals who have respiratory or circulatory conditions. Despite its ability to measure blood oxygen levels, a pulse oximeter is not designed to detect atrial fibrillation (AFib).
AFib is a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by an abnormal快速的心率达到100 to 150次/分钟,且心跳不规则。 AFib can occur concomitantly with other heart conditions and can lead to stroke, heart failure, and other complications.
While AFib is a significant health concern, a pulse oximeter is not a diagnostic tool for detecting AFib. Instead, to detect AFib, medical practitioners typically use EKG machines, which record electrical activity of the heart, to evaluate the electrical properties of the heart during a brief period of inactivity, which is known as an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).
It is important to note that a low blood oxygen level (hypoxemia) detected by a pulse oximeter may indicate that a patient has AFib or may be at risk of developing it due to other underlying health conditions. However, a pulse oximeter alone is not a reliable method for diagnosing AFib, and a healthcare provider should be consulted for any concerns or if a patient is experiencing symptoms related to AFib., a pulse oximeter is a device for monitoring blood oxygen levels but is not equipped to diagnose atrial fibrillation. To determine if a patient has AFib, healthcare professionals use specialized machines and心电图 exams that can assess the heart's electrical activity.