The human left foot is a intricate structure designed for balance, mobility, and support. It is divided into three main regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The hindfoot includes the talus and calcaneus bones, which work together to form the ankle joint. The midfoot is made up of five tarsal bones, including the navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiform bones, which provide stability to the arch of the foot. The forefoot consists of five metatarsal bones, which lead to the toes, and thirty-five phalanges, which make up the toes.
The foot is supported by many muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to enable movement. The major tendons include the calcanean tendinitis, which runs from the heel to the toes, and the tibialis anterior, which runs from the outer lower leg to the tarsals and first metatarsal, allowing dorsiflexion.
The plantar fascia is a strong, fibrous tissue that runs from the heel to the toes, forming the arch of the foot. It provides support for the arch and helps with balance. The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament connects the calcaneus to the navicular, while the calcaneocuboid ligament connects the calcaneus to the cuboid.
The toes are moved by several smaller muscles, including the flexor hallucis longus and brevis, which assist in flexing the great toe and the four lesser toes, respectively. These muscles are innervated by the deep peroneal nerve.
The nerves of the foot include the deep peroneal nerve, which controls the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg and provides sensation to the area between the first and second toes, and the sural nerve, which runs from the posterior aspect of the talar body to the lateral aspect of the foot and provides sensation to the outside of the foot.
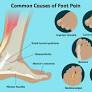
Foot problems can arise from a variety of reasons, including overuse, injury, and congenital abnormalities. Common foot problems include plantar fasciitis, bunions, flat feet, heel spurs, mallet toe, metatarsalgia, claw toe, and Morton's neuroma. These conditions can cause pain and的限制 mobility if not treated promptly. treatments can range from over-the-counter pain relievers to custom orthoses or shoes, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery.