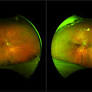
A horseshoe tear, also known as a flap tear, occurs when the vitreous humor within the eye pulls on the sensory retina at the edge of a tear and lifts it away from the retinal wall. This can potentially cause a retinal detachment if the tear remains unfixed.
Overview
- Definition: A small tear in the retina that extends into the vitreous humor.
- Occurrence: Commonly caused by progressive aging and posterior vitreous detachment (PVD).
- Risk Factors: Advanced age, myopia (nearsightedness), lattice degeneration, trauma, family history of retinal tears or detachment, and prior eye surgery.
- Symptoms: May include flashes of light, floaters, blurring of vision, or a shadow that covers the field of vision. A medical emergency if accompanied by a curtain-like floaters or darkness.
- Treatment: Usually requires laser photocoagulation or cryotherapy to create adhesion around the tear and prevent further detachment.
Causes
- Natural Aging: As the eye ages, the vitreous humor contracts, and its traction on the retina can cause small tears.
- PVD (Posterior Vitreous Detachment): A common condition where the vitreous separates from the retina, often without symptoms but can contribute to retinal tears.
- Trauma: Eye trauma can also lead to retinal tears, especially in individuals with pre-existing retinal issues.
Diagnosis
A retinal tear is typically diagnosed during a comprehensive eye examination by a retina specialist using techniques like scleral depression and fundus photography. In some cases, ophthalmic ultrasound may be necessary to aid in diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of a horseshoe tear focuses on preventing further retinal detachment. This is usually done using one of the following methods:
- Laser photocoagulation: A laser is applied around the tear to create adhesion between the retina and the retinal wall, effectively treating the tear.
- Cryotherapy (Freezing Therapy): Using a probe chilled to -20°C, the area around the tear is frozen to create an adhesion that prevents fluid from accumulating behind the retina.
- Pneumatic Retinopexy: This procedure involves inflating a small bubble under the retina to create pressure that holds the retinal tissue in place while the tear heals.
Prognosis
With appropriate treatment, most horseshoe tears do not progress to retinal detachment. Nevertheless, individuals with horseshoe tears are advised to monitor their eyes regularly for any signs of complications or further tear formation. Regular follow-up visits with an ophthalmologist are crucial to ensure optimal visual outcomes following treatment.
Discussing the Risks
The potential risks associated with horseshoe tears include the possibility of retinal detachment. While the risk is increased after a tear occurs, it is not certain that a horseshoe tear will eventually lead to detachment. Discussing the risks and benefits of treatment with an eye doctor is essential to make informed decisions about care.
Seeking Medical Attention
In the event of any retinal tear symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. A retinal tear can progress to retinal detachment, a medical emergency that requires urgent treatment to prevent significant visual impairment. If you suspect you have a retinal tear or have any concerns regarding your eye health, please schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment., a horseshoe tear is a type of retinal tear that occurs when the vitreous humor pulls on the sensory retina. While most tears heal themselves without treatment, some may require medical intervention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prognosis of horseshoe tears is essential for taking care of your eyes. If you have any questions or concerns regarding your eye health, please consult with an ophthalmologist for guidance and treatment.
Thismarkdown article is for information purposes only and should not be used as a basis for medical diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your healthcare provider for medical advice and treatment.