The human heart is a remarkable organ that lies at the base of the mediastinum, surrounded by a layer of serous pericardium. It is a pumping machine that pumps blood to all parts of the body, providing oxygen and nutrients while carrying away carbon dioxide and other waste products.
Overview of the Heart's Structure
The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right atrium receives blood from the body, while the left atrium receives blood from the lungs. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, while the left ventricle pumps blood to the rest of the body.
At the top of the heart is the superior vena cava, which carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium. The inferior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from the legs back to the right atrium. The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava enter the right atrium, joining it to the right ventricle.
Labeling the Chambers and Valves
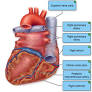
Now let's label the chambers and valves of the heart. The right upper chamber is the right atrium, labeled 1. The lower right chamber is the right ventricle, labeled 2. A tricuspid valve, labeled 3, prevents blood from flowing backward from the right ventricle into the right atrium. A pulmonary valve, labeled 4, prevents blood from flowing backward from the right atrium into the right ventricle as the ventricle contracts.
The left upper chamber is the left atrium, labeled 5. The lower left chamber is the left ventricle, labeled 6. A mitral valve, labeled 7, prevents blood from flowing backward from the left atrium into the left ventricle. A aortic valve, labeled 8, Prevents blood from flowing backward from the left ventricle into the left atrium as the ventricle contracts.
Labeling the血管与血液流动
Finally, let's label the blood vessels and the direction of blood flow. The superior vena cava, labeled 9, carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium. The inferior vena cava, labeled 10, brings deoxygenated blood from the legs back to the right atrium. The right atrium, labeled 11, sends deoxygenated blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The right ventricle, labeled 12, pumps deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, labeled 13, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
The left atrium, labeled 14, sends oxygenated blood through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. The left ventricle, labeled 15, pumps oxygenated blood through the aortic valve into the aorta, labeled 16, which carries oxygenated blood to the body.
The cardiovascular system is a complex network of organs and vessels that work together to transport blood and nutrients throughout the body. The heart, lungs, and blood vessels are the cornerstone of this system, working in harmony to ensure the circulation of deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation and the transportation of oxygenated blood throughout the body.
Conclusion
Remember, if you have any additional questions or need further clarification on any of the topics covered in this article, feel free to ask in the comment section.