Bartholin gland cysts, also known as bartholin cysts, are a common condition that affects the Bartholin glands, which are situated on either side of the vaginal opening. These small glands secrete mucus to help keep the area lubricated and are important for sexual intimacy. However, when these glands become swollen or block, they can lead to the formation of cysts.
Symptoms and History
Most women with Bartholin gland cysts are asymptomatic and do not experience any symptoms. However, some may notice a lump or discomfort in the vaginal area. In rare cases, if a Bartholin gland cyst becomes infected, it can lead to an abscess, which may cause additional symptoms such as fever, painful肿胀, and purulent discharge.
The diagnosis of Bartholin gland cysts is often made through a physical examination, during which the doctor may feel the swelling or tension in the area. An ultrasound is another common way to detect these cysts, as they appear as rounded, well-circumscribed masses in the lower part of the vagina.
Imaging Findings
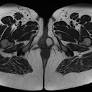
Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used to diagnose and evaluate Bartholin gland cysts. On ultrasound, the cysts appear as round or oval-shaped structures with smooth walls and varying amounts ofechoic content. In many cases, the cysts are filled with fluid and appear anechoic, meaning they do not contain solid components. However, when the cysts are infected or abscessed, they may demonstrate heterogenous echoes, indicating a complex structure with multiple echos from different phases of the menstrual cycle.
On T1-weighted images, Bartholin gland cysts may appear as varied echo patterns due to their content, including fluid, granulation tissue, or fibrosis. In addition, they may enhance pericystically after the administration of gadolinium-based contrast media, indicating inflammation or an abscess. On T2-weighted images, the cysts often display uniform hyperintensity due to the high protein content of cerebrospinal fluid, making the images more hyperintense.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for Bartholin gland cysts includes other gynecological conditions that may present with similar imaging findings, such as bartholin gland abscess and neoplasms. Abscesses are typically associated with more acute symptoms and may show increased vascularity on imaging. Neoplasms are more likely to be solid mass in the vestibule and may show variable contrast enhancement.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for Bartholin gland cysts typically focuses on resolving the symptoms and preventing complications. Conservative measures are often recommended initially, including warm sitz baths, analgesics, and gentle stretching exercises to help relax the surrounding muscles. If symptoms persist or worsen, aspiration or incision and drainage may be considered. Aspiration is a less invasive option that involves inserting a needle into the cyst to drain out the contents under direct visualization. In contrast, incision and drainage involves a larger incision for direct access to the gland. After drainage, a drain may be placed to facilitate healing. Recurrence rates can be high, requiring further treatment in some cases.
Bartholin gland cysts are a common occurrence in the reproductive years and are generally benign. Understanding the imaging characteristics and the appropriate management strategies is crucial for the effective diagnosis and treatment of these cysts. Asymptomatic cysts are commonly managed conservatively, but further evaluation may be necessary if symptoms develop or if there is a concern for a more complex process.Radiologists play a vital role in the diagnostic work-up and management of Bartholin gland cysts, and knowledge of their imaging findings and potential complications will continually evolve with advances in medical technology.