Bartholin cyst radiology: An overview
Introduction
A Bartholin cyst, also known as a Bartholin gland cyst, is a common妇科 condition that affects the Bartholin gland, which is located in the lower_third of the vaginal area. The gland produces mucus to keep the area moist and to help with fertility. Bartholin cysts typically develop due to blockages in the Bartholin gland's drainage tube, often caused by infection, inflammation, or trauma.
Radiology Case
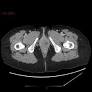
A 40-year-old female patient presented to the hospital with complaints of a swelling in the left lower third of her vagina/vulva. On physical examination, a fluctuating, thin-walled cystic lesion was observed in the left posterolateral aspect of the lower third of the vagina/vulva. An ultrasound was performed to assess the nature of the lesion.
Imaging Findings
The ultrasound revealed a well-defined, mostly anechoic cystic lesion with clear demarcation from the surrounding tissues. The lesion was located in the deep third of the vulva, inferior to the pubic symphysis, and appeared to be communicating with the Bartholin gland duct. The walls of the cyst were echoes and demonstrated varying echogenicity patterns, with areas of increased echogenicity consistent with inflammatory changes. There was no evidence of any suspicious lymphadenopathy or metastatic disease.
Differential Diagnosis
Bartholin cysts can be confused with other vulvovaginal masses such as Bartholin gland abscess, Bartholin gland tumor, Gartner duct cyst, Nabothian cyst, Skene's duct cyst, and urethral diverticulum.
Treatment and Prognosis
Most Bartholin cysts are asymptomatic and resolve spontaneously. However, if they become painful or complicated by infection, treatment may be necessary. Conservative treatments include pain management, warm soaks, and warm compresses. If the cyst is infected, oral antibiotics may be given. In cases where conservative measures fail, surgical drainage can be performed either by incision and drainage or with the insertion of a balloon catheter into the Bartholin gland duct. Recurrent cysts may require further interventions such as marsupialization.
##Bartholin cysts are a common妇科 condition that can be diagnosed using imaging techniques like ultrasound. Understanding the typical radiological appearance of Bartholin cysts is essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate management. With proper treatment, most Bartholin cysts can be effectively managed and may never cause significant distress or complications.