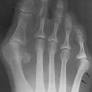
Tailor's bunion, also known as a bunionette, is a common foot condition characterized by a prominent bump on the外侧 5th metatarsal head, typically caused by shoe wear. While not as common as bunions on the inside of the foot, tailor's bunions can cause significant discomfort and may require treatment.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of a tailor's bunion is a bulge on the lateral aspect of the 5th metatarsal head, which may appear red, swollen, and painful. This bump can become more prominent when the foot is worn tight shoes, such as high heels or pointy toes.
Etiology
Tailor's bunions can be hereditary, resulting from an anomaly in the structural support of the foot. However, they can also occur due to factors such as an inverted foot (the outer edge of the foot is turned inward), loose ligaments, a low-lying 5th metatarsal bone, or tight leg muscles.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of tailor's bunion typically involves a physical examination and x-rays to visualize the bones and soft tissues of the foot. X-rays can also be helpful in determining the exact cause of the deformity and planning for appropriate treatment.
Management
Treatment for tailor's bunion can vary based on the severity of the condition and the response to nonoperative measures. Nonoperative treatment is often the first line of treatment, including:
- Shoe Wear Modification: Choosing shoes with a wide toe box, avoiding pointed toes, and opting for lower heels can help reduce pressure on the 5th metatarsal head.
- Padding: Bunion pads can be placed over the area to reduce friction and pain.
- Oral Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Icing: Applying an ice pack to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- ** Injection Therapy**: Corticosteroid injections can be given to reduce inflammation around the joint.
- Custom Orthotics: Custom orthotic devices may be recommended to correct abnormal foot mechanics and provide cushioning.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where nonoperative treatment fails or the deformity is severe, surgical correction may be necessary. This can include a lateral condylectomy, distal metatarsal osteotomy, or a combination of procedures.
Prognosis
The prognosis for tailor's bunion treatment varies based on factors such as age, activity level, and the severity of the deformity. With proper treatment, most tailor's bunions can be successfully managed and corrected. Recurrence rates are generally low, but it is important to follow up with a foot and ankle orthopaedic specialist if signs of recurrence are present.
Conclusion
Tailor's bunion is a common foot condition that can cause significant discomfort. The exact cause of the deformity can vary, but the condition can often be managed with nonoperative measures. Severe cases may require surgical intervention, but overall, tailor's bunions can be successfully treated and corrected with appropriate follow-up and management.