VEINS OF THE CHEST
The chest is the central hub of the circulatory system, serving as the primary route for blood and oxygen to flow from the heart to the rest of the body. It is a complex network of vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, all working in harmony to ensure the efficient delivery of necessary elements like oxygen and nutrients.
ANATOMY OF THE CHEST
The chest wall is composed of several bones, including the costo-vertebral joints, which are essential for supporting the weight of the upper limbs and providing stability to the ribs. The sternum, or breastbone, is a long, flat bone that protects the heart and lungs. Between the ribs, the intercostal muscles run in cranial-caudal rows, providing support and movement to the chest wall.
Key components of the chest walls' vasculature include:
-
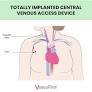
Superior Vena Cava (SVC): The superior vena cava is the main vein that brings deoxygenated blood from the head, arms, and chest wall to the right atrium of the heart.
-
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC): The inferior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from the lower extremities, pelvis, and abdominal organs to the right atrium.
-
Pulmonary Arteries: These arteries carry oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
-
Pulmonary Veins: These veins carry deoxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium.
-
Thoracic Aorta: The thoracic aorta supplies blood to the anterior, middle, and posterior aspects of the thoracic wall.
CLINICAL IMPORTANCE OF CHEST VEINS
Chest veins are important in both medical and surgical contexts. In medical emergencies, they can become occluded due to blood clots, leading to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). These conditions can be very serious and require immediate treatment.
In surgical settings, chest veins are often accessed for the insertion of central venous catheters (CVTs), which are used for administering medications, drawing blood samples, or providing temporary pacing. Proper positioning of these catheters is crucial to minimize the risk of complications, such as infection or air embolism.
The chest wall also acts as a structural support for the heart, protecting it from the force exerted during contraction. Any injury or disease that affects the chest wall can significantly impact heart function.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR CHEST VEINS
Treatment for chest veins typically focuses on managing symptoms and improving circulation. Options include:
-
Conservative treatments: These include lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding sedentary behaviors, and reducing the risk of blood clots (e.g., by avoiding oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy).
-
Venous duplex ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test evaluates the velocity and direction of blood flow in the chest veins, aiding in the diagnosis of vein disease.
-
Sclerotherapy: This technique involves the injection of a chemical into the affected vein, which causes the vein to collapse and eventually disappear. It is often used for varicose veins in the legs but can also be applied to chest walls.
-
Endovenous laser therapy: Similar to sclerotherapy, endovenous激光治疗是通过插入光纤到受影响的静脉内,利用激光能量使静脉收缩和闭合。
-
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: This procedure uses radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy the affected veins.
-
Thoracentesis:
- An invasive procedure in which a doctor removes excess fluid from the pleural space using smaller incisions.
- Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS):
- A less invasive alternative to traditional thoracentesis, VATS involves smaller incisions and an endoscope to aid in the removal or repair of disorders within the thoracic cavity.
- Chest wall reconstruction: In cases of severe chest wall injury or disease, surgical reconstruction may be required to restore normal chest wall function.
Thoracentesis is a medical procedure that involves inserting a needle into the pleural space to remove excess fluid. This fluid, known as pleural effusion, can accumulate for various reasons, including heart failure, infections, or malignant tumors.
Endovenous laser therapy (ELT) is a less invasive surgical procedure used to treat vein insufficiency in the legs by delivering laser energy through a flexible catheter into the affected veins. The laser heat stimulates the inner layer of the vein to contract and close, effectively shrinking the vessel and eliminating the need for surgical intervention.
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is another less invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy the targeted veins, leading to their occlusion and improved circulation.
Thoracoscopy is a medical imaging technology that uses smaller incisions to aid in minimally invasive surgical procedures within the chest space. The surgeon uses an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera, to aid in the切除 of damaged lung tissue or other conditions within the chest wall.
Chest wall reconstruction may be required in cases of severe injury or disease to the chest wall, involving the骨骼, muscles, or soft tissues.重建手术的目的是修复或替换受损的组织结构, restoring normal chest wallfunction and providing adequate support to the heart and lungs.
CONCLUSION
Understanding the anatomy and function of veins within the chest is crucial for diagnosing and treating conditions such as DVT, PE, and varicose veins. With advancements in medical technology and techniques, management of chest veins has become more targeted and effective, leading to better patient outcomes.
Thoracentesis, endovenous laser therapy, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation, VATS, and chest wall reconstruction are vital tools in the medical community'stoolkit for addressing chest vein concerns. By choosing the appropriate treatment option, chest vein health can be preserved, and patients can regain confidence in their ability to lead active, everyday lives.
This article was designed with a focus on the clinical importance of chest veins, their diagnosis and treatment options, and the medical terminology associated with them. It aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of chest vein anatomy, the various conditions that can affect them, and the latest advancements in treatment methods.