: A Review on its Potential Role in Respiratory Medicine
Glutathione, commonly known as GSH, is an essential thiolic compound present in几乎所有的生物体中. Its role in maintaining cellular redox balance is crucial, as it plays a pivotal part in regulating various biological processes. The importance of glutathione in health and disease has been extensively studied, particularly in the context of oxidant stress, where this compound acts as a powerful antioxidant. However, the delivery of glutathione molecules to the lungs, where the majority of diseases affect, has been a challenge due to its low solubility and instability in aqueous environments. This has led to the development of nebulized glutathione – a liquid formulation of glutathione designed to enhance its bioavailability and therapeutic potential by facilitating its direct uptake into the lungs.
What is Nebulized Glutathione?
Nebulized glutathione, or more formally known as 'nebulized reduced glutathione', refers to the inhalation of glutathione molecules through the use of a nebulizer, which breaks down the drug into smaller particles that can be inhaled into the lungs. The advantages of nebulized formulations include ease of use, as they are generally portable, and the ability to deliver precise amounts of medication directly to the site of interest within the lungs. This is particularly useful in the treatment of respiratory conditions, where direct access to the lungs is essential.
Mechanisms of Action
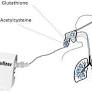
The lung is an ideal target for the delivery of nebulized glutathione due to its extensive_surface_area and the presence of a rich network of alveolar macrophages, which are capable of phagocytosing and breaking down foreign particles. When glutathione is inhaled, these macrophages are equipped to uptake and break down the molecules, releasing the active compound into the bloodstream. This process is further complemented by the pulmonary endothelial cells, which are responsible for the permeability of the lungs, allowing the glutathione to reach the bloodstream and be distributed to various organs, including the lungs themselves.
The potential roles of nebulized glutathione in respiratory medicine are diverse. It has been shown to have antioxidant properties, protecting the lungs from氧化ative stress caused by various insults. Glutathione also has anti-inflammatory effects, which could be beneficial in the treatment of respiratory illnesses characterized by neutrophilia. Additionally, it has been postulated to modulate immune responses and facilitate the resolution of inflammatory processes in the lungs.
Clinical Studies and Observations
Clinical trials have been conducted to assess the safety and efficacy of nebulized glutathione in various respiratory conditions. In patients with cystic fibrosis, a genetic disease characterized by abnormal chloride channel function, nebulized glutathione has been shown to improve lung function and reduce the need for additional oxygen therapy. Similarly, in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), nebulized glutathione has been associated with improved respiratory symptoms and a higher quality of life, as assessed by the Saint-George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ).
While most studies have been promising, a few notable limitations have been noted. To date, no controlled clinical trials have been conducted in individuals with COVID-19, making it difficult to draw directs regarding the role of nebulized glutathione in this setting. However, given the potential benefits of antioxidants in reducing inflammation and improving oxygenation, further investigation into the potential role of nebulized glutathione in the management of COVID-19 is certainly warranted.
Precautions and Applications
Given the potential for systemic absorption and the risk of toxicity associated with high systemic doses of glutathione, careful consideration must be given to the appropriate dosing regimen when using nebulized preparations. However, when used under the dosing guidelines established by healthcare professionals, nebulized glutathione shows promise as a safe and effective treatment option for a variety of respiratory conditions.—-
Nebulized glutathione is a new therapeutic option with the potential to alter the treatment landscape in respiratory medicine. Its role in improving respiratory function in various respiratory conditions is promising, and ongoing research will help to further define its role in the management of lung diseases. However, as with any new treatment modality, careful consideration must be given to the potential benefits versus the associated risks, and a comprehensive approach to care must be taken to ensure the safe and effective use of nebulized glutathione in clinical practice.