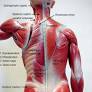
Muscle model labeling is a fundamental skill in the field of anatomical modeling and visualization. It involves the process of assigning specific labels or annotations to individual muscles or muscle groups within a model. These labels serve to identify the location, shape, and function of each muscle, which is crucial for understanding the complexities of human anatomy and musculoskeletal system.
Overview
Muscle labeling is a critical component of biological modeling, particularly in the development of medical devices, surgical simulations, and educational resources. Accurate muscle labeling is essential for generating realistic simulations that can be used for research, training, and clinical applications. It is also a key element in creating visualizations that aid in the understanding of muscle functions and interactions within the human body.
Objectives
The primary objective of muscle modeling and labeling is to establish a standardized framework that accurately represents the human body's muscularsystem. This framework should include the names, locations, shapes, and functions of each muscle, as well as their attachments, innervations, and relationships with other解剖结构. By providing this detailed information, muscle models become a powerful tool for education, research, and clinical application.
Key Concepts
Muscle labeling incorporates several key concepts that are essential for accurate and informative models:
-
肌肉名称: Each muscle in the model must be assigned a unique name that accurately reflects its identity and location within the body.
-
位置: The position of each muscle relative to other解剖结构 must be clearly defined. This includes the origin, insertion, and surface landmarks of the muscle.
-
形状: The shape of each muscle must be accurately represented in the model, ensuring that it accurately matches the actual muscle shape in the body.
-
功能: Each muscle's function should be clearly marked, providing insight into how it interacts with other muscles and the rest of the body.
-
连接部位: The points where muscles attach to other bones or bones must be identified and labeled, along with any connections to神经或血管。
-
神经分布: The nerves that supply each muscle must be accurately depicted, showing their course and connections to the central nervous system.
-
解剖关系: It is important to maintain the解剖 relationships between different muscle groups and their surrounding structures.
Methodology
Creating muscle models with accurate labels involves a series of steps:
-
数据收集: Collect accurate and detailed information about the human musculoskeletal system, including muscle names, locations, shapes, functions, attachments, innervations, and connections.
-
模型创建: Use specialized software tools to create a 3D model of the human body, including muscles, bones, and other解剖结构.
-
肌肉标记: Add labels to the model to represent the identified muscle features, using standardized naming conventions.
-
验证和修正: Review the labeled model to ensure accuracy and completeness, making any necessary revisions or adjustments.
Challenges
Muscle labeling presents several challenges, including:
-
复杂性: The human musculoskeletal system is highly complex, with thousands of muscles and connective tissues. Accurate labeling requires a deep understanding of their functions and relationships.
-
一致性: Muscle labeling must be consistent across different models and datasets to be useful for comparison and analysis.
-
标准化: Developing and maintaining a standardized labeling scheme that accurately represents muscle features across different datasets can be difficult.
-
软件工具的选择: Selecting the right software tools and algorithms for muscle labeling can be challenging due to variations in their capabilities and features.
-
训练和专业知识: Mastery of muscle labeling requires specialized training in anatomical modeling, computer graphics, and visual assessment skills.
##Muscle model labeling is a vital skill that underpins the creation of sophisticated anatomical models and visualizations. By following the principles outlined in this article, developers and researchers can achieve consistent and accurate muscle labeling, enabling the creation of models that are both accurate and useful for educational and clinical purposes.