In this article, we will discuss the concept of horseshoe tears in the retina, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We will also explore the factors that determine the risk of developing horseshoe retinal detachment (RRD).
Horseshoe Tears in the Retina
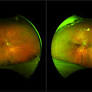
A horseshoe tear is a retinal tear that forms in the upper corner of the eye, just outside the inferior quadrant. This type of tear is characterized by a 'flap'-like appearance, resembling a horseshoe. Horseshoe tears are most commonly caused by the abnormal pull of the vitreous humor (the clear gel that fills the space behind the eye) on the retina.
Causes
The primary cause of horseshoe tears is the natural aging process of the eye. As we age, the vitreous humor begins to contract and pull away from the retina. Thistraction can sometimes cause the retina to tear in a horsehoe shape. Other factors that increase the risk of developing a horseshoe tear include:
- Advanced age: As we age, the vitreous humor becomes more liquid and more likely to pull away from the retina.
- Nearsightedness (Myopia): People who are nearsighted have a stronger convexity in their透镜, which can cause the vitreous humor to attach better to the nasal side of the retina, increasing the risk of a horseshoe tear.
- Lattice Degeneration: A condition where there are thin patches in the retina, which can make it more prone to tears.
- Trauma: Previous eye trauma can increase the risk of developing a horseshoe tear.
- Family History of Retinal Tears or Detachment: Having a family member with a history of retinal tears or detachment increases the risk of developing the condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a horseshoe tear may include:
*闪光感 (Photopsia): A feeling of bright lights or闪烁 in the field of vision.
*飞蚊症 (Floaters): Small, round spots or strands in the vision, which may look like shadows or cobwebs.
*遮挡视线 (Shadowing): A dark, curtain-like shadow or veil across part of the field of vision.
*视力模糊 (Blurred Vision): Objects may appear distorted or blurred due to the pressure from the accumulated fluid under the retina.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of a horseshow tear is typically made using a slit-lamp microscope and panoramic retinal photography. Treatment typically involves a laser photocoagulation or cryopexy to seal the tear and prevent retinal detachment.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for developing a horseshoe tear include advanced age, nearsightedness, lattice degeneration, trauma, and family history of retinal tears or detachment.
##Horseshoe tears in the retina are a common cause of retinal detachment, a serious eye disease that can lead to blindness if not treated promptly. It is important for individuals who are at high risk of developing horseshoe tears to seek regular eye exams and follow-up care with an ophthalmologist. Treatments such as laser photocoagulation or cryopexy can effectively repair horseshoe tears and prevent retinal detachment.
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule an appointment, please call us at [Phone Number] or visit our website at [Website URL].