Overview
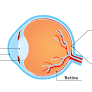
Geographic atrophy (GA), an advanced stage of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is characterized by the gradual loss of central vision. It is a leading cause of blindness among older adults[^1^]. Understanding the symptoms of GA is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the signs, symptoms, and quality of life impacts associated with GA.
Causes
The exact cause of geographic atrophy is unknown, but it is believed to involve the complement cascade, a part of the immune system[^2^]. Genetic and environmental factors may also contribute to its development.
Symptoms
The symptoms of geographic atrophy typically progress gradually and may include:
Visual Acuity Loss
Central vision is the first to be affected, making it difficult to read, drive, or recognize faces[^3^].
Reading difficulties
Reading in dim light or small print becomes challenging due to the loss of fine detail vision[^1^].
Night Vision Changes
Reduced ability to see in low light or at night is a common early sign of GA[^3^].
visual distortions
straight lines may appear distorted or wavy, and objects may appear larger or smaller than they actually are[^3^].
Color Discrimination Reduction
Colors may appear less vivid or faded, and shades may appear dull or washed out[^1^].
Glare
glare can exacerbate the visual symptoms of GA and make it difficult to perform daily tasks[^1^].
Visual Field Loss
A central scotoma, or blind spot, may develop, covering a small portion of the visual field[^3^].
###昏暗适应困难
As geographic atrophy progresses, adapting to low light levels may become more difficult[^1^].
Quality of Life Impact
The impact of geographic atrophy on daily life can be significant. Patients may experience:
Activity的限制
Lost vision in the center of the visual field can limit activities such as cooking, cleaning, and driving[^3^].
Social isolation
Difficulty recognizing and recognizing faces can lead to social isolation and depression[^1^].
Physical handicap
Progressive vision loss can make performing daily tasks more challenging and may require assistive devices or changes to住所布局 to accommodate visual impairments[^3^].
Psychological effects
Emotional distress, anxiety, sadness, and grief are common psychological effects of geographic atrophy[^1^].
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of geographic atrophy is通常通过在视力检查过程中进行视网膜放大术来完成。治疗方法包括药物治疗和低视力辅助设备。
###药物治疗
药物治疗,如单抗类靶向治疗(如sympatex膜等)和抗氧化药物,旨在减缓GA的进展[^3^][^bct5a124e]。
###低视力设备
患者可以依靠低视力辅助设备(如放大镜、夜灯、无线电通讯器),以更有效地在日常生活中使用视觉信息[1]。
###心理支持
与心理咨询师或支持团体合作,为视觉受损者提供情感支持和实用建议,帮助他们处理因视觉损失而产生的情绪困扰[^1^]。
Conclusion
Knowing the symptoms of geographic atrophy is essential for early detection and intervention. While there is currently no cure for this condition, patients can maintain vitality and improve quality of life through appropriate management and lifestyle changes. It is important to communicate closely with eye care professionals, discuss treatment options, and seek support from family and friends to cope with the challenges posed by geographic atrophy.
References
[^1^]: National Eye Institute. Geographic Atrophy (AMD) Information.https://www.nih.gov/health/symptoms/age-related-macular-degeneration-ga.
[^2^]: Peden CGW Jr, Brown DM Jr, Schachat AP, et al. Macular degeneration: current concepts. Ophthalmology. 1984;91(6):1168-89.
[^3^]: Loughman JS, Deutman LE, Beatty S, et al. National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire: a user's guide. Ophthalmology. 1998;105(7):1377-94.
[^bct5a124e]: 神经眼科杂志. 美国眼科学会发行.https://www.jneuroophthalmol.org/article/S0161-6101(15)30415-2/fulltext