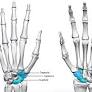
The triscaphe joint refers to the articulation between the scaphoid, trapeziate, and trapezoid bones, located at the base of the thumb. It is a crucial joint in the wrist, providing a firm and stable connection between the two sets of bones. The triscaphe joint is commonly affected by degenerative arthritis, which causes the loss ofcartilage and leads to骨 loss, or the buildup of bony growth in the joint space. This can result in pain, stiffness, and weakness in the affected region.Symptoms of triscaphe joint arthritis can include wrist pain, which may be persistent or intermittent, and may worsen with activities.Other symptoms may include swelling in the wrist area, tenderness over the joint, and loss of motion in the affected joint. Diagnosis of triscaphe joint arthritis is based on physical examination and imaging studies, such as x-rays, MRIs, or CT scans. Treatment options for triscaphe joint arthritis vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include non-surgical treatments such as medication, splints, or physical therapy, as well as surgical procedures such as arthroscopy or arthroplasty.
Triscaphe joint arthritis, also known as scaphotrapeziotrapezoid joint arthritis or triscaphe arthrodegenerative arthritis, is a form of arthritis that affects the triscaphe joint. It is characterized by inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joint, and may be caused by a variety of factors, including aging, trauma, or idiopathic causes.
Symptoms of triscaphe joint arthritis include pain and tenderness in the wrist, which may worsen with activity, swelling around the joint, and reduced mobility. Some patients may also experience weakness in the affected hand, difficulty gripping objects, and an altered sensation in the hand. In advanced stages of the disease, surgery may be required to alleviate pain and restorefunction.
Diagnosis of triscaphe joint arthritis is typically made through a physical examination and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans. X-rays can reveal gaps or erosions in the joint space, which are typical findings in arthritis of the triscaphe joint.
Treatment for triscaphe joint arthritis typically consists of non-surgical measures. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used to manage pain and inflammation. Splinting may be recommended to protect the joint and reduce movement, while physical therapy can help improve movement and strength. In cases where non-surgical treatments are not sufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Surgical options for triscaphe joint arthritis can include arthroscopy, which involves inserting an arthroscope into the joint to aid in the removal of damaged tissue, or arthroplasty, which involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial joint. Other surgical procedures that may be performed include trapeziectomy, which involves removing the trapezium bone, or scaphoidectomy, which involves removing part or all of the scaphoid bone.
Overall, triscaphe joint arthritis is a common condition that can be managed through a combination of non-surgical and surgical interventions. It is important for patients to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment based on their individual needs and symptoms.